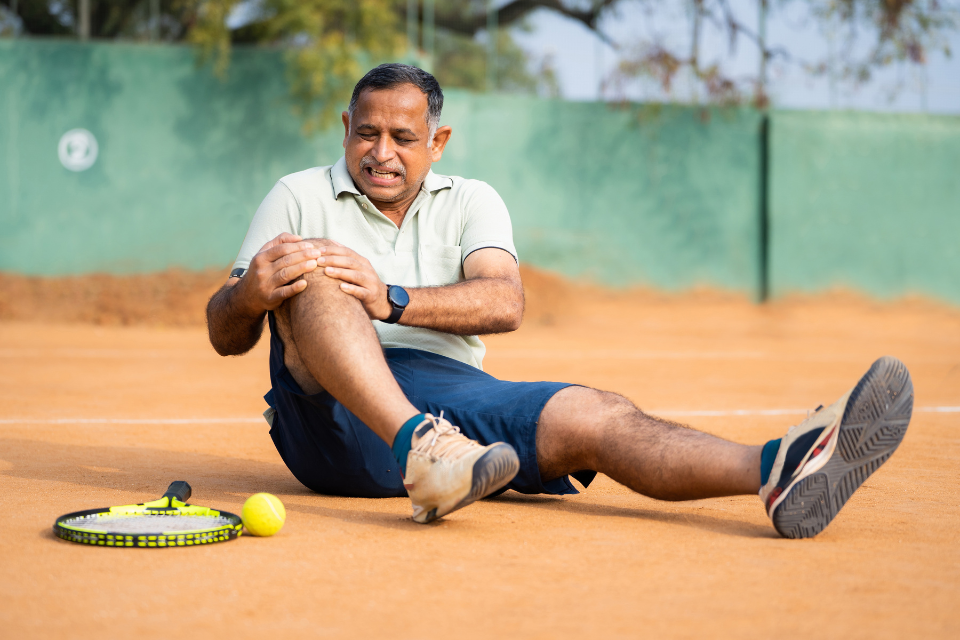
Athletes often push their bodies to the limit, subjecting their knees to immense stress and strain during rigorous training and competition. Knee pain is a prevalent issue among athletes, impacting performance and posing challenges to their sports careers. Understanding the causes, preventive measures, and effective management strategies for knee pain in athletes is crucial in optimizing athletic performance and ensuring long-term joint health.
- Common Causes of Knee Pain in Athletes:
- Overuse and Repetitive Stress: The nature of athletic training involves repetitive movements, such as running, jumping, or pivoting, leading to overuse injuries like patellar tendinitis or IT band syndrome.
- Acute Injuries: Sports-related incidents like ligament tears (ACL, MCL), meniscus tears, or fractures due to sudden twists, impacts, or falls can cause severe knee pain.
- Improper Biomechanics: Faulty movement patterns or biomechanical issues can put undue stress on the knees, leading to pain and injuries.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weakness or imbalance in the muscles surrounding the knee can affect stability and increase the risk of injuries.
- Preventive Measures for Athletes:
- Proper Training Techniques: Coaches and trainers should emphasize correct form, adequate warm-ups, and gradual progression in training routines.
- Strength and Conditioning: Incorporating strength training exercises targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes to enhance knee stability and support.
- Cross-Training and Rest Days: Diversifying workouts and incorporating rest days into training schedules to prevent overuse injuries.
- Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Prompt Medical Evaluation: Athletes experiencing persistent knee pain should seek immediate evaluation by sports medicine professionals to diagnose and treat underlying issues.
- RICE Protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation can help alleviate acute pain and swelling post-injury.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches under the guidance of a physical therapist aid in rehabilitation and strengthening.
- Bracing or Supportive Gear: Depending on the injury, using supportive braces or taping techniques may offer stability and pain relief.
- Return to Sport and Long-Term Management:
- Gradual Return to Activity: Athletes should follow a structured rehabilitation program before returning to full activity to prevent re-injury.
- Continued Strength and Mobility Work: Maintaining a regimen of exercises that focus on strength, flexibility, and stability around the knee is crucial for long-term management.
- Mental Health and Support:
- Dealing with injuries and chronic knee pain can impact an athlete’s mental well-being. Seeking support from sports psychologists or counselors can aid in coping with challenges.
Knee pain is a common challenge faced by athletes, but with proper understanding, preventive strategies, and appropriate management, athletes can overcome these obstacles. Emphasizing correct training techniques, prompt diagnosis, rehabilitation, and ongoing maintenance play pivotal roles in managing knee pain among athletes.