A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, leading to the deprivation of oxygen and nutrients. This sudden interruption can have severe consequences, affecting various bodily functions and leading to long-term disabilities. Understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and recovery from a stroke is crucial in raising awareness and aiding prevention.
- Types of Strokes:
- Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blockage in a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain, accounting for the majority of stroke cases.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Occurs due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain, leading to bleeding and increased pressure on brain tissues.
- Common Risk Factors:
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension is a leading risk factor for strokes, damaging blood vessels and increasing the risk of clots or ruptures.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption elevate stroke risk due to their impact on blood vessels and overall health.
- Diabetes and High Cholesterol: These conditions contribute to arterial damage, leading to increased stroke susceptibility.
- Sedentary Lifestyle and Poor Diet: Lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating habits significantly increase stroke risk.
- Recognizing Symptoms:
- Sudden Numbness or Weakness: Especially on one side of the body, often in the face, arm, or leg.
- Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech: Slurred speech or confusion.
- Trouble Walking or Coordination Issues: Dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination problems.
- Immediate Response and Treatment:
- Act FAST: Recognize facial drooping, arm weakness, and speech difficulty; if these symptoms arise, it’s time to call emergency services.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: Ischemic stroke treatment may involve clot-dissolving medications if administered promptly.
- Surgery or Interventional Procedures: Hemorrhagic strokes may require surgery to repair damaged blood vessels or relieve pressure on the brain.
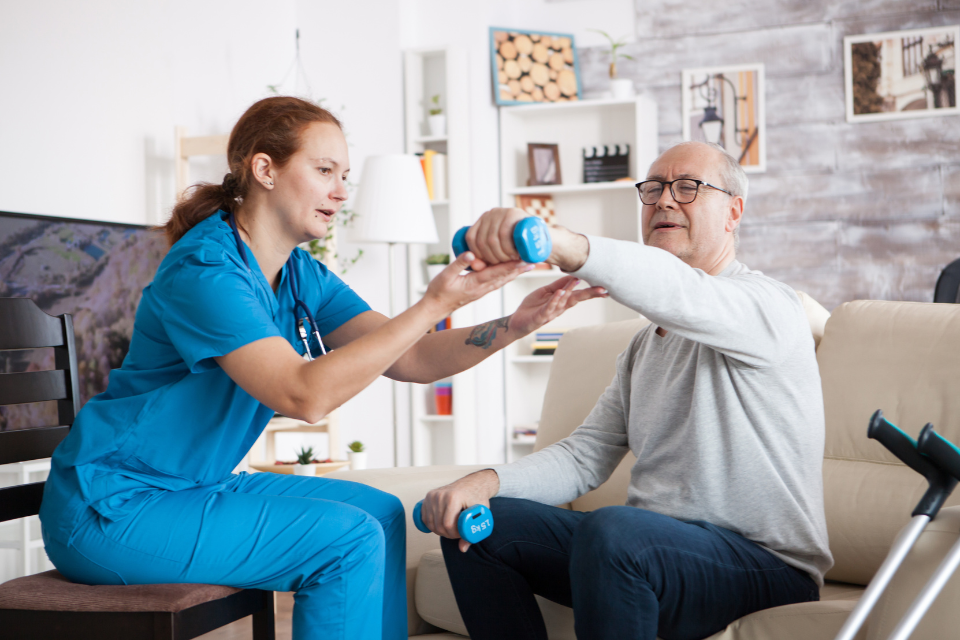
- Post-Stroke Recovery:
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy aid in recovery and relearning skills.
- Medication and Lifestyle Changes: Medications to manage risk factors like blood pressure, cholesterol, and lifestyle modifications are crucial.
- Support Networks: Building a supportive environment with family, caregivers, and support groups is integral to the emotional and physical recovery process.
- Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications:
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats and sodium intake.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to maintain cardiovascular health.
- Manage Health Conditions: Regular check-ups, medication adherence, and managing underlying health conditions are vital.
Strokes are a serious medical emergency, but awareness, prompt action, and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk and improve outcomes. Understanding the warning signs, seeking immediate medical attention, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to stroke prevention and aid in post-stroke recovery.